Russian Scientists Develop New Compound for Treating Aggressive Tumours

A team of Russian researchers has synthesised a novel compound for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), a treatment for advanced cancer that uses the boron-10 isotope. The compound exhibits low toxicity, excellent water solubility, and eliminates the need for administering large volumes. Most importantly, the active substance reaches the tumour with minimal impact on healthy tissues. The study was published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences shortly before World Cancer Day, observed annually on February 4.
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) is an advanced cancer treatment that leverages the properties of the boron-10 isotope. The method involves first saturating tumour cells with boron-10, followed by irradiation with thermal neutrons. This triggers a nuclear reaction that selectively destroys cancer cells while sparing healthy tissue. Thus, the treatment success largely depends on the compound's ability to effectively deliver boron-10 to the tumour and maintain the necessary boron concentration.
A team of scientists from the HSE Faculty of Chemistry, the Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry of the Russian Academy of Sciences, and the N.N. Blokhin National Medical Research Centre of Oncology has developed three compounds that combine the closo-dodecaborate anion with amino acids containing a side-chain amino group. The molecules are structurally similar to natural amino acids, allowing them to 'trick' the body's transport systems into capturing and delivering them to cells, including cancer cells. This makes the substance effective at targeting tumours, where it accumulates.
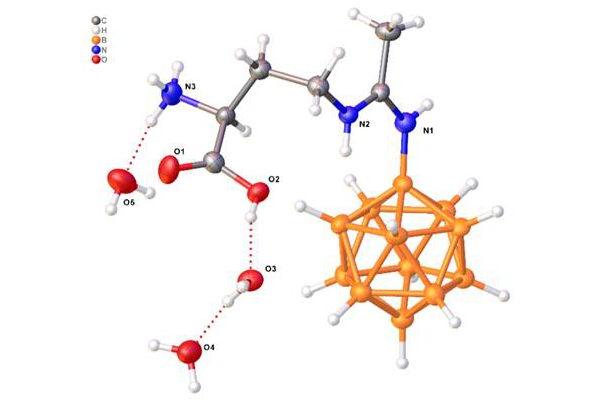
One of the compounds demonstrated low toxicity, with the half-lethal dose (LD50) for experimental animals ranging from 150 to 300 mg per kilogram of body weight. In experiments, the compound not only demonstrated the ability to accumulate boron in tumour tissues but also confirmed its effectiveness in animals. When administered to laboratory mice, the boron concentration in melanoma tumour cells was six times higher than in healthy tissues after 45 minutes.
The compound can exist in two forms depending on the pH level. The first form is a sodium salt, which is highly soluble in water under conditions close to physiological pH, making it convenient for therapeutic use. The second form occurs upon acidification, when the compound transforms into an insoluble internal salt useful for obtaining a medically pure product during the stages of synthesis, isolation, and purification.

Margarita Ryabchikova
'The aim of the study was to reduce toxicity and simplify the compound purification process, building on data from previous research. As a result, three new compounds were synthesised. One of them exhibited optimal characteristics: it does not cause significant side effects when administered intravenously and dissolves well in water, setting it apart from existing therapeutic drugs,' explains study author Margarita Ryabchikova, a third-year student at the HSE Faculty of Chemistry. 'We aimed not only for high efficacy but also for production convenience. The developed method can be easily scaled to produce the required quantities of the product while remaining economically viable.'
The study demonstrated that the new compound accumulates more effectively in the tissues of certain types of tumours compared to the currently used drug. This is an important step toward developing a safer and more accessible therapy. The research is still in its early stages, but this development has the potential to significantly improve cancer treatment outcomes and broaden the applications of boron neutron capture therapy in the fight against various types of tumours.
See also:
Larger Groups of Students Use AI More Effectively in Learning
Researchers at the Institute of Education and the Faculty of Economic Sciences at HSE University have studied what factors determine the success of student group projects when they are completed with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). Their findings suggest that, in addition to the knowledge level of the team members, the size of the group also plays a significant role—the larger it is, the more efficient the process becomes. The study was published in Innovations in Education and Teaching International.
New Models for Studying Diseases: From Petri Dishes to Organs-on-a-Chip
Biologists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the Kulakov National Medical Research Centre for Obstetrics, Gynecology, and Perinatology, have used advanced microfluidic technologies to study preeclampsia—one of the most dangerous pregnancy complications, posing serious risks to the life and health of both mother and child. In a paper published in BioChip Journal, the researchers review modern cellular models—including advanced placenta-on-a-chip technologies—that offer deeper insights into the mechanisms of the disorder and support the development of effective treatments.
Using Two Cryptocurrencies Enhances Volatility Forecasting
Researchers from the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences have found that Bitcoin price volatility can be effectively predicted using Ethereum, the second-most popular cryptocurrency. Incorporating Ethereum into a predictive model reduces the forecast error to 23%, outperforming neural networks and other complex algorithms. The article has been published in Applied Econometrics.
Administrative Staff Are Crucial to University Efficiency—But Only in Teaching-Oriented Institutions
An international team of researchers, including scholars from HSE University, has analysed how the number of non-academic staff affects a university’s performance. The study found that the outcome depends on the institution’s profile: in research universities, the share of administrative and support staff has no effect on efficiency, whereas in teaching-oriented universities, there is a positive correlation. The findings have been published in Applied Economics.
Physicists at HSE University Reveal How Vortices Behave in Two-Dimensional Turbulence
Researchers from the Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and the HSE University's Faculty of Physics have discovered how external forces affect the behaviour of turbulent flows. The scientists showed that even a small external torque can stabilise the system and extend the lifetime of large vortices. These findings may improve the accuracy of models of atmospheric and oceanic circulation. The paper has been published in Physics of Fluids.
Solvent Instead of Toxic Reagents: Chemists Develop Environmentally Friendly Method for Synthesising Aniline Derivatives
An international team of researchers, including chemists from HSE University and the A.N. Nesmeyanov Institute of Organoelement Compounds of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INEOS RAS), has developed a new method for synthesising aniline derivatives—compounds widely used in the production of medicines, dyes, and electronic materials. Instead of relying on toxic and expensive reagents, they proposed using tetrahydrofuran, which can be derived from renewable raw materials. The reaction was carried out in the presence of readily available cobalt salts and syngas. This approach reduces hazardous waste and simplifies the production process, making it more environmentally friendly. The study has been published in ChemSusChem.
How Colour Affects Pricing: Why Art Collectors Pay More for Blue
Economists from HSE University, St Petersburg State University, and the University of Florida have found which colours in abstract paintings increase their market value. An analysis of thousands of canvases sold at auctions revealed that buyers place a higher value on blue and favour bright, saturated palettes, while showing less appreciation for traditional colour schemes. The article has been published in Information Systems Frontiers.
New Method for Describing Graphene Simplifies Analysis of Nanomaterials
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has proposed a new mathematical method to analyse the structure of graphene. The scientists demonstrated that the characteristics of a graphene lattice can be represented using a three-step random walk model of a particle. This approach allows the lattice to be described more quickly and without cumbersome calculations. The study has been published in Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and Theoretical.
Scientists Have Modelled Supercapacitor Operation at Molecular and Ionic Level
HSE scientists used supercomputer simulations to study the behaviour of ions and water molecules inside the nanopores of a supercapacitor. The results showed that even a very small amount of water alters the charge distribution inside the nanopores and influences the device’s energy storage capacity. This approach makes it possible to predict how supercapacitors behave under different electrolyte compositions and humidity conditions. The paper has been published in Electrochimica Acta. The study was supported by a grant from the Russian Science Foundation (RSF).
Designing an Accurate Reading Skills Test: Why Parallel Texts are Important in Dyslexia Diagnosis
Researchers from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for accurately assessing reading skills in adults with reading impairments. It can be used, for instance, before and after sessions with a language therapist. The tool includes two texts that differ in content but are equal in complexity: participants were observed to read them at the same speed, make a similar number of errors, and understand the content to the same degree. Such parallel texts will enable more accurate diagnosis of dyslexia and better monitoring of the effectiveness of interventions aimed at addressing it. The paper has been published in Educational Studies.


